In recent years, the practice of yoga has gained immense popularity worldwide as a holistic approach to physical and mental well-being. Every year on June 21st, people from all walks of life come together to celebrate International Yoga Day. This day serves as a reminder of the profound benefits yoga offers, and the ancient wisdom it encapsulates. In this blog, we will delve into the origins of yoga, its historical significance, and the transformative power that has made it a global phenomenon.
- Blogs
- General-knowledge
- International-yoga-day-embracing-the-ancient-path-to-wellness-6492877e14e5bf000127e5cb
International Yoga Day: Embracing the Ancient Path to Wellness
General Knowledge • 21 Jun, 2023 • 13,583 Views • ⭐ 5.0
Written by Shivani Chourasia

The Origin of Yoga

Yoga, derived from the Sanskrit word "yuj," meaning union or connection, traces its roots back over 5,000 years to ancient India. The earliest mention of Yoga can be found in the sacred texts of the Rigveda, where it is described as a means to attain spiritual enlightenment. The practice of Yoga was further developed and systematized by the sage Patanjali in his compilation of the Yoga Sutras, considered the foundational text of classical Yoga.
Historical Significance

Throughout history, Yoga has been an integral part of Indian culture and spirituality. It has been practised by sages, ascetics, and seekers of truth for millennia. The ancient Indian sage, Maharishi Patanjali, codified the principles and practices of Yoga in his Yoga Sutras around the 2nd century BCE. These sutras encompass the Eight Limbs of Yoga, known as Ashtanga, which provide a comprehensive guide for leading a purposeful and harmonious life.
The Eight Limbs of Yoga
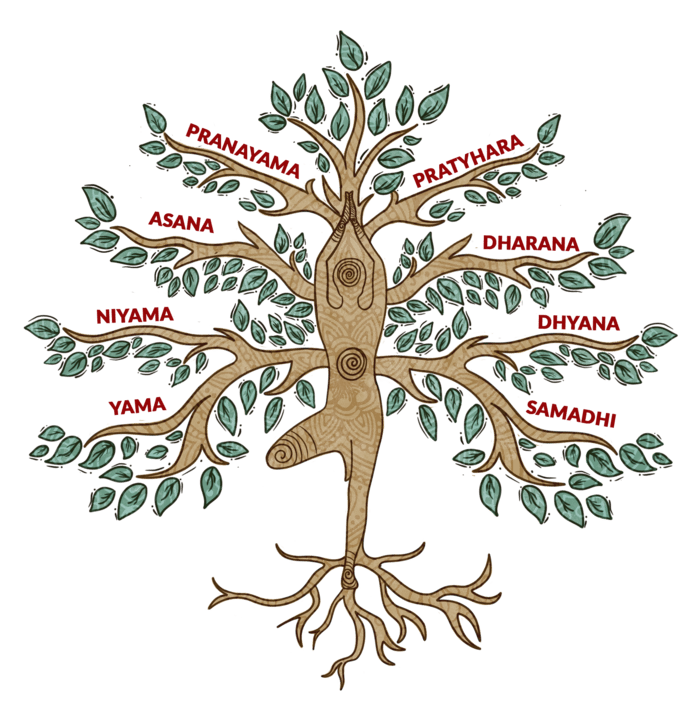
The Eight Limbs of Yoga serve as a roadmap for individuals seeking a balanced and fulfilling existence. They include:
- Yama: Universal moral principles such as non-violence, truthfulness, and non-greed.
- Niyama: Personal observances like purity, contentment, and self-discipline.
- Asana: Physical postures that promote strength, flexibility, and balance.
- Pranayama: Breath control techniques that enhance vital energy and cultivate mindfulness.
- Pratyahara: Withdrawal of the senses to turn inward and achieve mental stillness.
- Dharana: Concentration exercises to focus and discipline the mind.
- Dhyana: Meditation practices that lead to a state of profound awareness and inner peace.
- Samadhi: The ultimate goal of Yoga, is a state of blissful union with the divine.